Developing hierarchical anticipations via neural network-based event segmentation
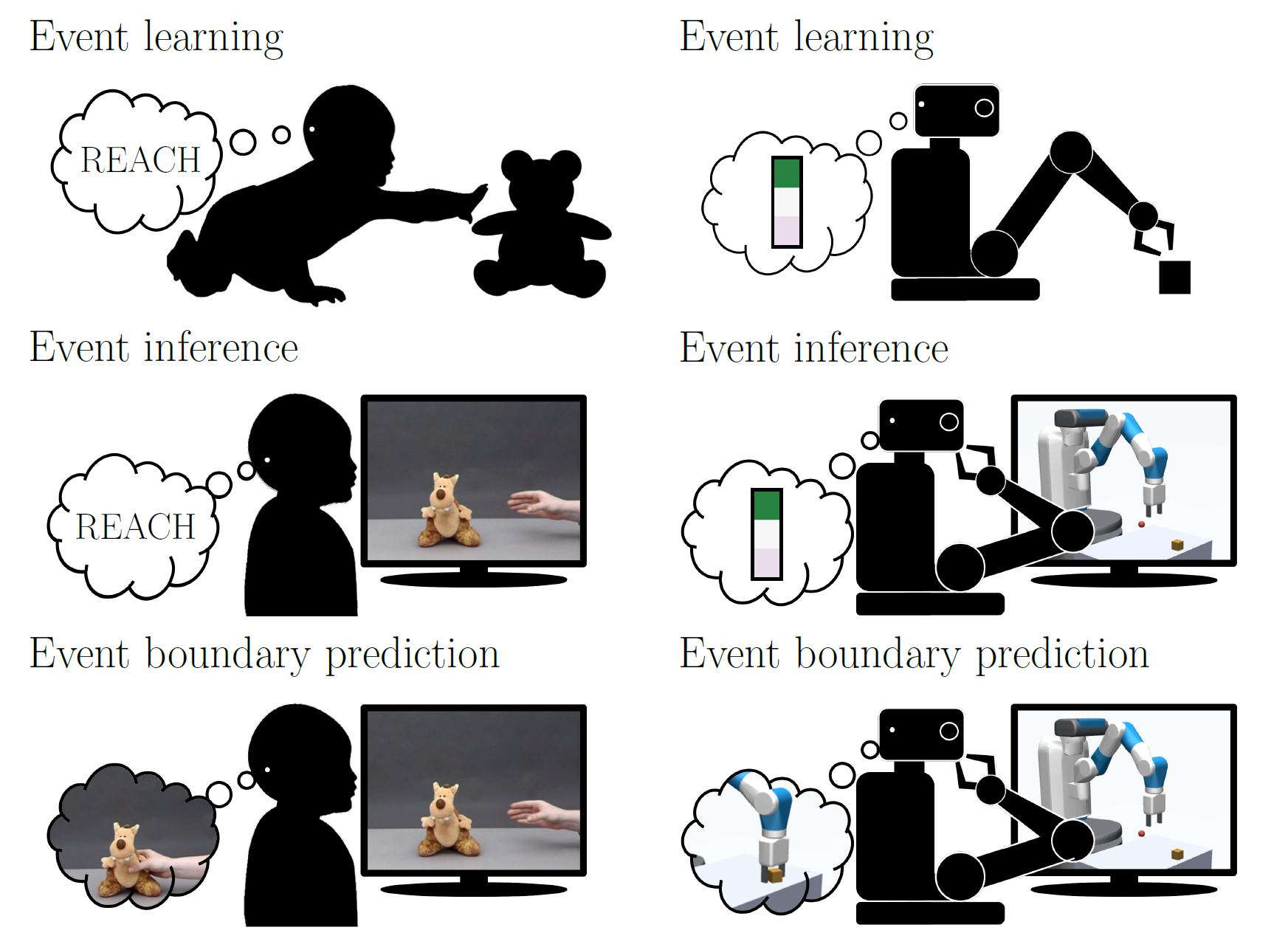
Humans can make predictions on various time scales and hierarchical levels. Thereby, the learning of event encodings seems to play a crucial role. In this work we model the development of hierarchical predictions via autonomously learned latent event codes. We present a hierarchical recurrent neural network architecture, whose inductive learning biases foster the development of sparsely changing latent state that compress sensorimotor sequences. A higher level network learns to predict the situations in which the latent states tend to change. Using a simulated robotic manipulator, we demonstrate that the system (i) learns latent states that accurately reflect the event structure of the data, (ii) develops meaningful temporal abstract predictions on the higher level, and (iii) generates goal-anticipatory behavior similar to gaze behavior found in eye-tracking studies with infants. The architecture offers a step towards the autonomous learning of compressed hierarchical encodings of gathered experiences and the exploitation of these encodings to generate adaptive behavior.
| Award: | (SmartBot Challenge award winner) |
| Author(s): | Christian Gumbsch and Maurits Adam and Birgit Elsner and Georg Martius and Martin V Butz |
| Book Title: | Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL 2022) |
| Pages: | 1-8 |
| Year: | 2022 |
| Month: | September |
| Bibtex Type: | Conference Paper (inproceedings) |
| Event Name: | 2022 IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL) |
| URL: | https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02042 |
| Award Paper: | SmartBot Challenge award winner |
| Electronic Archiving: | grant_archive |
BibTex
@inproceedings{gumbsch2022_hierarchical,
title = {Developing hierarchical anticipations via neural network-based event segmentation},
aword_paper = {SmartBot Challenge award winner},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL 2022)},
abstract = {Humans can make predictions on various time scales and hierarchical levels. Thereby, the learning of event encodings seems to play a crucial role. In this work we model the development of hierarchical predictions via autonomously learned latent event codes. We present a hierarchical recurrent neural network architecture, whose inductive learning biases foster the development of sparsely changing latent state that compress sensorimotor sequences. A higher level network learns to predict the situations in which the latent states tend to change. Using a simulated robotic manipulator, we demonstrate that the system (i) learns latent states that accurately reflect the event structure of the data, (ii) develops meaningful temporal abstract predictions on the higher level, and (iii) generates goal-anticipatory behavior similar to gaze behavior found in eye-tracking studies with infants. The architecture offers a step towards the autonomous learning of compressed hierarchical encodings of gathered experiences and the exploitation of these encodings to generate adaptive behavior. },
pages = {1-8},
month = sep,
year = {2022},
slug = {gumbsch2022},
author = {Gumbsch, Christian and Adam, Maurits and Elsner, Birgit and Martius, Georg and Butz, Martin V},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02042},
month_numeric = {9}
}

