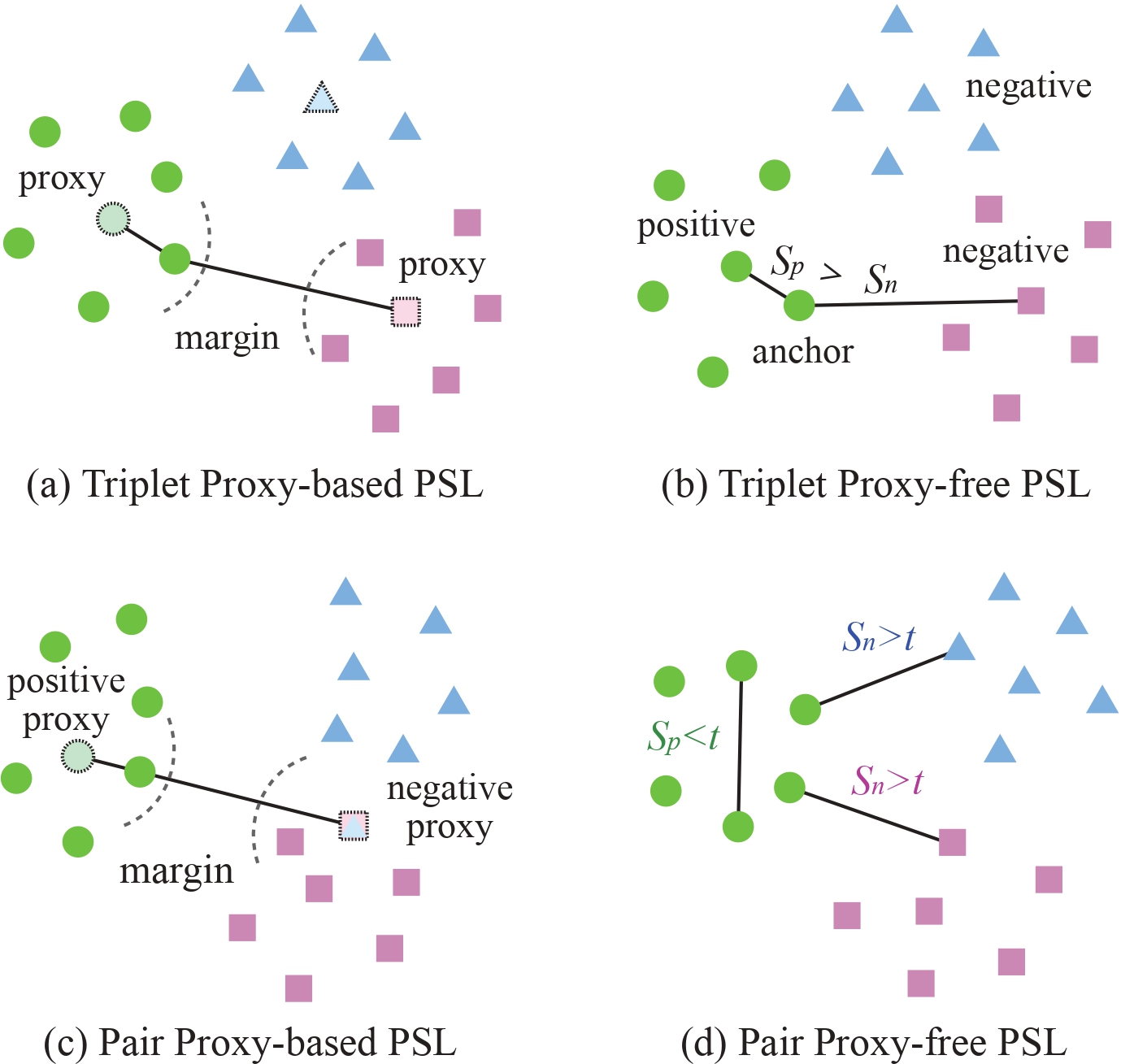
In this paper, we focus on a general yet important learning problem, pairwise similarity learning (PSL). PSL subsumes a wide range of important applications, such as open-set face recognition, speaker verification, image retrieval and person re-identification. The goal of PSL is to learn a pairwise similarity function assigning a higher similarity score to positive pairs (i.e., a pair of samples with the same label) than to negative pairs (i.e., a pair of samples with different label). We start by identifying a key desideratum for PSL, and then discuss how existing methods can achieve this desideratum. We then propose a surprisingly simple proxy-free method, called SimPLE, which requires neither feature/proxy normalization nor angular margin and yet is able to generalize well in open-set recognition. We apply the proposed method to three challenging PSL tasks: open-set face recognition, image retrieval and speaker verification. Comprehensive experimental results on large-scale benchmarks show that our method performs significantly better than current state-of-the-art methods.
| Author(s): | Wen, Yandong* and Liu, Weiyang* and Feng, Yao and Raj, Bhiksha and Singh, Rita and Weller, Adrian and Black, Michael J. and Schölkopf, Bernhard |
| Book Title: | Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) |
| Year: | 2023 |
| Month: | October |
| Bibtex Type: | Conference Paper (inproceedings) |
| Event Name: | International Conference on Computer Vision 2023 |
| Event Place: | Paris, France |
| State: | Published |
| URL: | https://simple.is.tue.mpg.de/ |
| Electronic Archiving: | grant_archive |
BibTex
@inproceedings{simple2023wen,
title = {Pairwise Similarity Learning is {SimPLE}},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
abstract = {In this paper, we focus on a general yet important learning problem, pairwise similarity learning (PSL). PSL subsumes a wide range of important applications, such as open-set face recognition, speaker verification, image retrieval and person re-identification. The goal of PSL is to learn a pairwise similarity function assigning a higher similarity score to positive pairs (i.e., a pair of samples with the same label) than to negative pairs (i.e., a pair of samples with different label). We start by identifying a key desideratum for PSL, and then discuss how existing methods can achieve this desideratum. We then propose a surprisingly simple proxy-free method, called SimPLE, which requires neither feature/proxy normalization nor angular margin and yet is able to generalize well in open-set recognition. We apply the proposed method to three challenging PSL tasks: open-set face recognition, image retrieval and speaker verification. Comprehensive experimental results on large-scale benchmarks show that our method performs significantly better than current state-of-the-art methods.},
month = oct,
year = {2023},
slug = {simple2023wen},
author = {Wen, Yandong* and Liu, Weiyang* and Feng, Yao and Raj, Bhiksha and Singh, Rita and Weller, Adrian and Black, Michael J. and Sch{\"o}lkopf, Bernhard},
url = {https://simple.is.tue.mpg.de/},
month_numeric = {10}
}




