Bioinspired Composite Microfibers for Skin Adhesion and Signal Amplification of Wearable Sensors
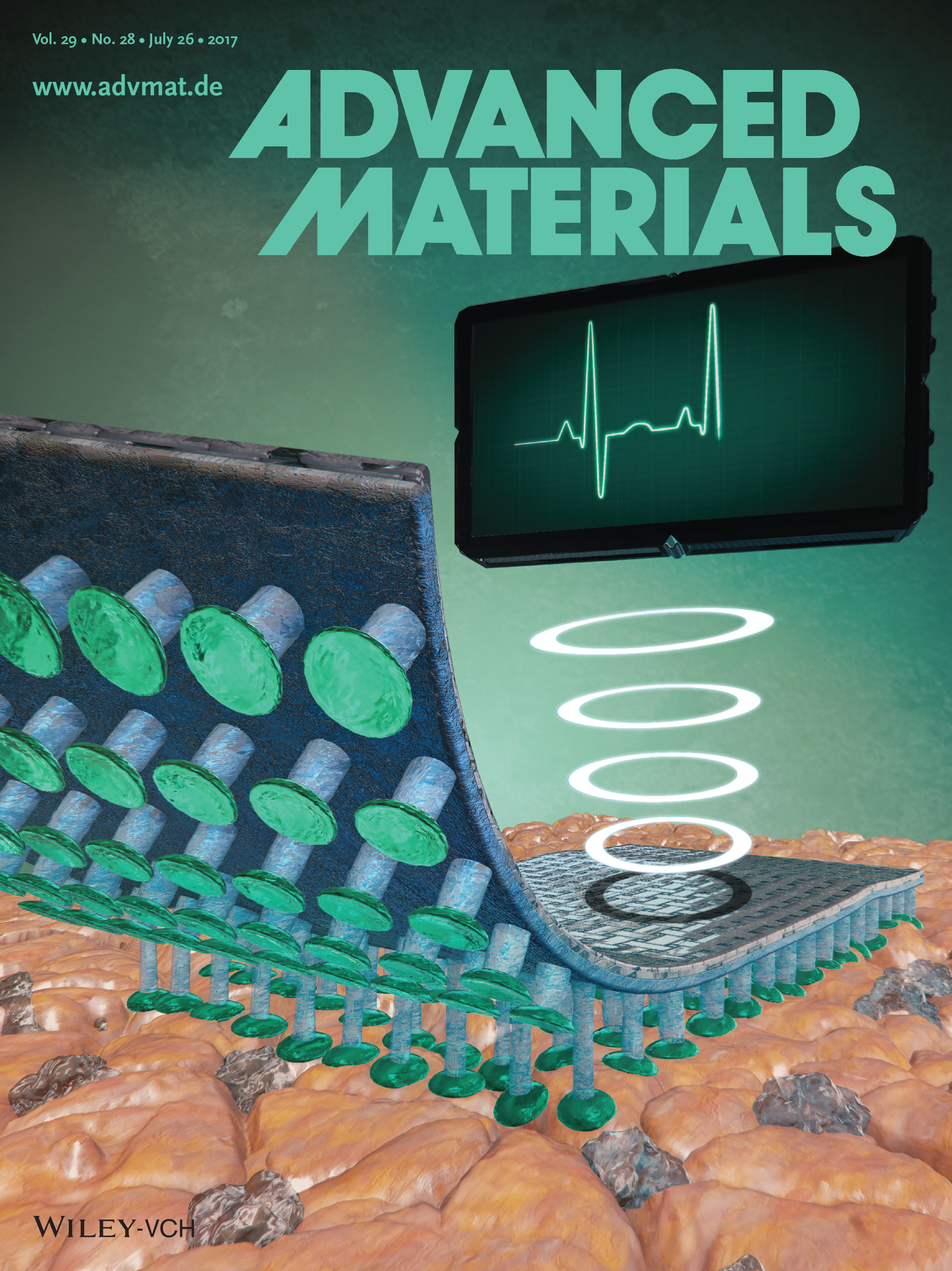
A facile approach is proposed for superior conformation and adhesion of wearable sensors to dry and wet skin. Bioinspired skin-adhesive films are composed of elastomeric microfibers decorated with conformal and mushroom-shaped vinylsiloxane tips. Strong skin adhesion is achieved by crosslinking the viscous vinylsiloxane tips directly on the skin surface. Furthermore, composite microfibrillar adhesive films possess a high adhesion strength of 18 kPa due to the excellent shape adaptation of the vinylsiloxane tips to the multiscale roughness of the skin. As a utility of the skin-adhesive films in wearable-device applications, they are integrated with wearable strain sensors for respiratory and heart-rate monitoring. The signal-to-noise ratio of the strain sensor is significantly improved to 59.7 because of the considerable signal amplification of microfibrillar skin-adhesive films.
| Author(s): | Drotlef, Dirk-M and Amjadi, Morteza and Yunusa, Muhammad and Sitti, Metin |
| Journal: | Advanced Materials |
| Volume: | 29 |
| Number (issue): | 28 |
| Pages: | 1701353 |
| Year: | 2017 |
| Bibtex Type: | Article (article) |
| DOI: | 10.1002/adma.201701353 |
| Electronic Archiving: | grant_archive |
BibTex
@article{drotlef2017bioinspired,
title = {Bioinspired Composite Microfibers for Skin Adhesion and Signal Amplification of Wearable Sensors},
journal = {Advanced Materials},
abstract = {A facile approach is proposed for superior conformation and adhesion of wearable sensors to dry and wet skin. Bioinspired skin-adhesive films are composed of elastomeric microfibers decorated with conformal and mushroom-shaped vinylsiloxane tips. Strong skin adhesion is achieved by crosslinking the viscous vinylsiloxane tips directly on the skin surface. Furthermore, composite microfibrillar adhesive films possess a high adhesion strength of 18 kPa due to the excellent shape adaptation of the vinylsiloxane tips to the multiscale roughness of the skin. As a utility of the skin-adhesive films in wearable-device applications, they are integrated with wearable strain sensors for respiratory and heart-rate monitoring. The signal-to-noise ratio of the strain sensor is significantly improved to 59.7 because of the considerable signal amplification of microfibrillar skin-adhesive films.},
volume = {29},
number = {28},
pages = {1701353},
year = {2017},
slug = {drotlef2017bioinspired},
author = {Drotlef, Dirk-M and Amjadi, Morteza and Yunusa, Muhammad and Sitti, Metin}
}