Autonomous Robotic Manipulation
Modeling Top-Down Saliency for Visual Object Search
Interactive Perception
State Estimation and Sensor Fusion for the Control of Legged Robots
Probabilistic Object and Manipulator Tracking
Global Object Shape Reconstruction by Fusing Visual and Tactile Data
Robot Arm Pose Estimation as a Learning Problem
Learning to Grasp from Big Data
Gaussian Filtering as Variational Inference
Template-Based Learning of Model Free Grasping
Associative Skill Memories
Real-Time Perception meets Reactive Motion Generation
Autonomous Robotic Manipulation
Learning Coupling Terms of Movement Primitives
State Estimation and Sensor Fusion for the Control of Legged Robots
Inverse Optimal Control
Motion Optimization
Optimal Control for Legged Robots
Movement Representation for Reactive Behavior
Associative Skill Memories
Real-Time Perception meets Reactive Motion Generation
Physics of Body Shape and Motion
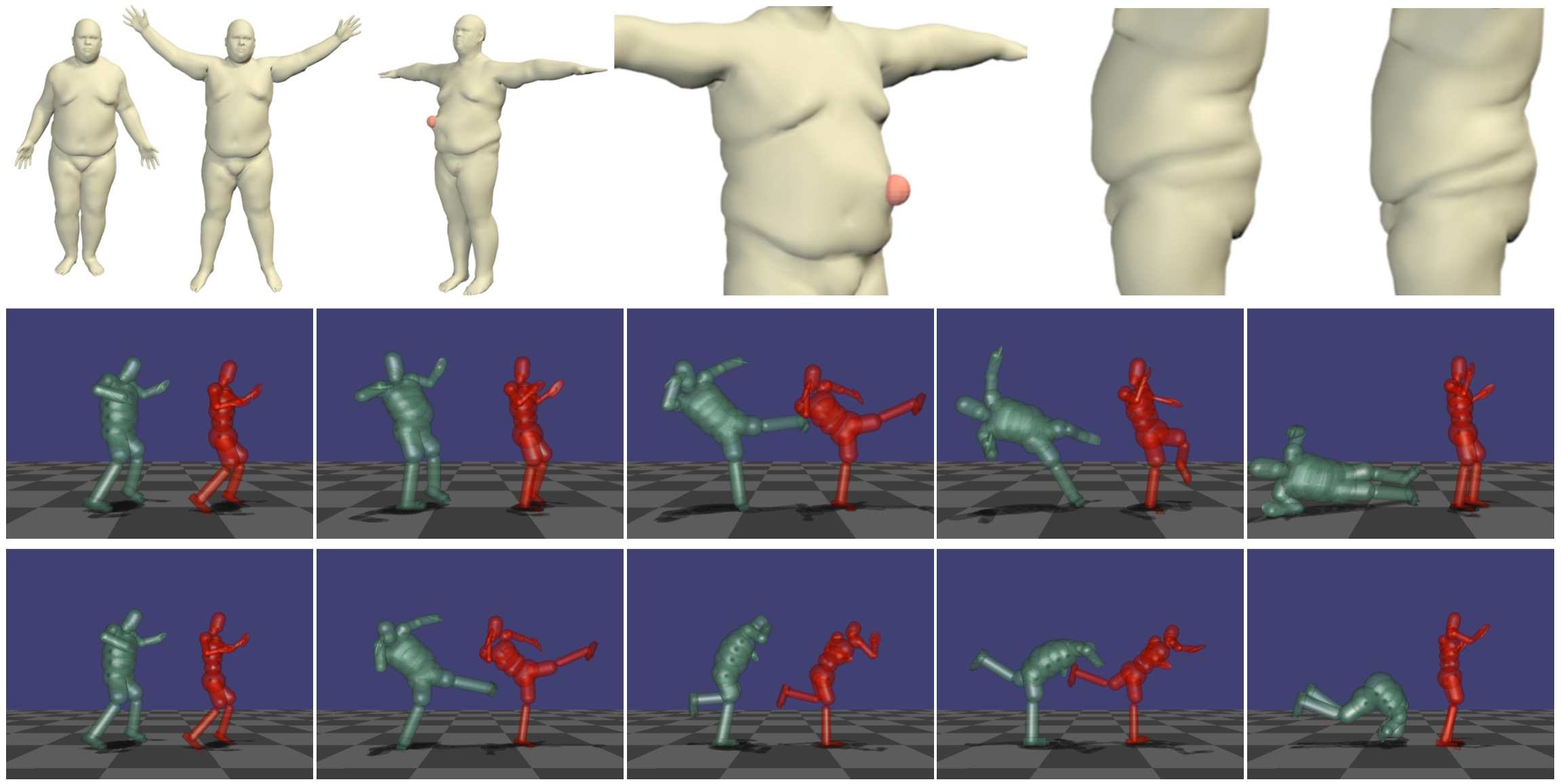
Humans live in a real world governed by the laws of physics; that is, we apply and exploit forces, such as gravity, in our daily interactions with the world. In this project we allow virtual humans to interact with a virtual world subject to the laws of physics. How would one's body shape deform in case of a collision with an object? How would our walk pattern look like if we weighed a few kilos more?
To model soft-tissue dynamics, we learn a layered volumetric body model from data []. To enable this we extend the triangulated mesh of the SMPL body model with a volumetric tetrahedral model called VSMPL. VSMPL contains an inner "rigid" layer and an outer soft-tissue layer. Given 4D sequences of people in motion, we learn the physical properties (Young's modulus) of the outer tetrahedra. We do this such that, when simulated in motion using a finite element method, the surface motion of the VSMPL model resembles the observations. The learned model is a realistic full-body avatar that generalizes to novel motions and external forces.
We also address the problem of retargeting the captured motion of one person onto a different person with a different body shape and physical properties (e.g.~taller, heavier, thinner) such that the new morphology is taken into account []. We obtain visually plausible simulations using a simplified representation of human body shape that we animate using physically-based retargeting. We develop a novel spacetime optimization approach that learns and robustly adapts physical controllers to new bodies and constraints. The method automatically adapts the motion to a subject with the novel target body shape, respecting the physical properties, and producing an appropriate movement. This makes it easy to create a varied set of motions from a single mocap sequence by simply varying the characters.
Members
Publications





