2025
ps
Gozlan, Y., Falisse, A., Uhlrich, S., Gatti, A., Black, M., Chaudhari, A.
OpenCapBench: A Benchmark to Bridge Pose Estimation and Biomechanics
In IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) , February 2025 (inproceedings)
sf
Wu, J., Abebe, R., Hardt, M., Stoica, A.
Policy Design in Long-run Welfare Dynamics
2025 (misc) Submitted
2024
ps
Baert, K., Bharadwaj, S., Castan, F., Maujean, B., Christie, M., Abrevaya, V., Boukhayma, A.
SPARK: Self-supervised Personalized Real-time Monocular Face Capture
In SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Proceedings, SIGGRAPH Asia 2024, December 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
rm
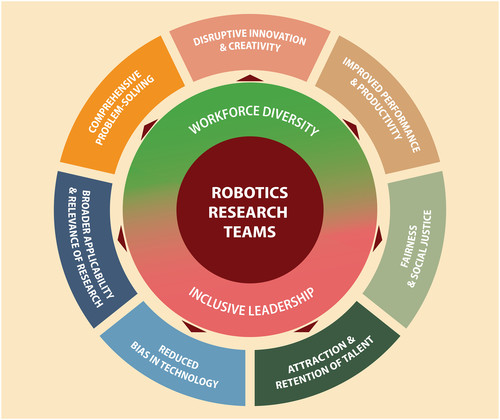
Macari, D., Fratzl, A., Keplinger, K., Keplinger, C.
Accelerating the pace of innovation in robotics by fostering diversity and inclusive leadership
Science Robotics, 9, December 2024 (article)
ps
Xiu, Y., Liu, Z., Tzionas, D., Black, M. J.
PuzzleAvatar: Assembling 3D Avatars from Personal Albums
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 43(6), ACM, December 2024 (article) To be published
ei
Didolkar, A. R., Goyal, A., Ke, N. R., Guo, S., Valko, M., Lillicrap, T. P., Rezende, D. J., Bengio, Y., Mozer, M. C., Arora, S.
Metacognitive Capabilities of LLMs: An Exploration in Mathematical Problem Solving
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Buchholz, S.
Learning partitions from Context
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Kapoor, J., Schulz, A., Vetter, J., Pei, F., Gao, R., Macke, J. H.
Latent Diffusion for Neural Spiking Data
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Rajendran*, G., Buchholz*, S., Aragam, B., Schölkopf, B., Ravikumar, P. K.
From Causal to Concept-Based Representation Learning
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Zhao, J., Singh, S. P., Lucchi, A.
Theoretical Characterisation of the Gauss Newton Conditioning in Neural Networks
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Allingham, J. U., Mlodozeniec, B. K., Padhy, S., Antoran, J., Krueger, D., Turner, R. E., Nalisnick, E., Hernández-Lobato, J. M.
A Generative Model of Symmetry Transformations
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Garrido, S., Blöbaum, P., Schölkopf, B., Janzing, D.
Causal vs. Anticausal merging of predictors
In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024) , 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
ei
Chen, W., Ge, H.
Neural Characteristic Activation Analysis and Geometric Parameterization for ReLU Networks
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024) , 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Dmitriev, D., Buhai, R., Tiegel, S., Wolters, A., Novikov, G., Sanyal, A., Steurer, D., Yang, F.
Robust Mixture Learning when Outliers Overwhelm Small Groups
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Lin, J. A., Padhy, S., Mlodozeniec, B. K., Antoran, J., Hernández-Lobato, J. M.
Improving Linear System Solvers for Hyperparameter Optimisation in Iterative Gaussian Processes
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024) , 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ps
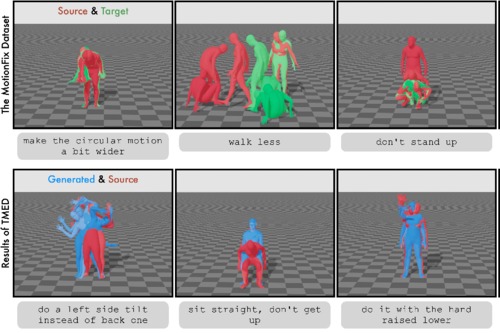
Athanasiou, N., Cseke, A., Diomataris, M., Black, M. J., Varol, G.
MotionFix: Text-Driven 3D Human Motion Editing
In SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Proceedings, ACM, December 2024 (inproceedings) To be published
ei
Piatti*, G., Jin*, Z., Kleiman-Weiner*, M., Schölkopf, B., Sachan, M., Mihalcea, R.
Cooperate or Collapse: Emergence of Sustainability in a Society of LLM Agents
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024, *equal contribution (conference) Accepted
ei
Jain, S., Lubana, E. S., Oksuz, K., Joy, T., Torr, P., Sanyal, A., Dokania, P. K.
What Makes Safety Fine-tuning Methods Safe? A Mechanistic Study
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Vetter, J., Moss, G., Schröder, C., Gao, R., Macke, J. H.
Sourcerer: Sample-based Maximum Entropy Source Distribution Estimation
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ps
Ye, C., Qiu, L., Gu, X., Zuo, Q., Wu, Y., Dong, Z., Bo, L., Xiu, Y., Han, X.
StableNormal: Reducing Diffusion Variance for Stable and Sharp Normal
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 43(6), ACM, December 2024 (article) To be published
ei
Guo, S., Zhang, C., Muhan, K., Huszár*, F., Schölkopf*, B.
Do Finetti: On Causal Effects for Exchangeable Data
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024, *joint senior authors (conference) Accepted
ei
Chan, R., Bourmasmoud, R., Svete, A., Ren, Y., Guo, Q., Jin, Z., Ravfogel, S., Sachan, M., Schölkopf, B., El-Assady, M., Cotterell, R.
On Affine Homotopy between Language Encoders
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Pals, M., Sağtekin, A. E., Pei, F., Gloeckler, M., Macke, J.
Inferring stochastic low-rank recurrent neural networks from neural data
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024) , 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2024 (conference) Accepted
hi
Mohan, M., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Demonstration: OCRA - A Kinematic Retargeting Algorithm for Expressive Whole-Arm Teleoperation
Hands-on demonstration presented at the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Munich, Germany, November 2024 (misc) Accepted
al
hi
ei
Andrussow, I., Sun, H., Martius, G., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Demonstration: Minsight - A Soft Vision-Based Tactile Sensor for Robotic Fingertips
Hands-on demonstration presented at the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Munich, Germany, November 2024 (misc) Accepted
hi
Bartels, J. U., Sanchez-Tamayo, N., Sedlmair, M., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Active Haptic Feedback for a Virtual Wrist-Anchored User Interface
Hands-on demonstration presented at the ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST), Pittsburgh, USA, October 2024 (misc) Accepted
OS Lab
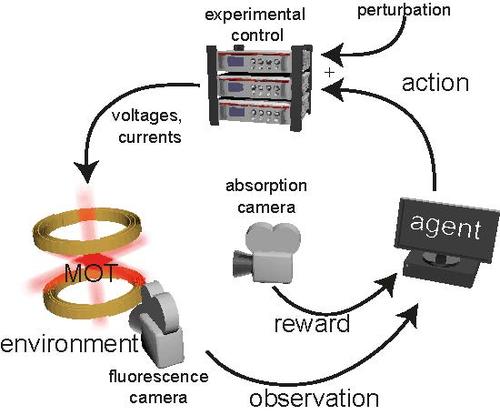
Reinschmidt, M., Fortágh, J., Günther, A., Volchkov, V.
Reinforcement learning in cold atom experiments
nature communications, 15:8532, October 2024 (article)
ps
Zakharov, E., Sklyarova, V., Black, M. J., Nam, G., Thies, J., Hilliges, O.
Human Hair Reconstruction with Strand-Aligned 3D Gaussians
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, October 2024 (inproceedings)
sf
Sigg, D., Hardt, M., Mendler-Dünner, C.
Decline Now: A Combinatorial Model for Algorithmic Collective Action
arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.12633, October 2024 (conference) Submitted
ncs
ps
Ostrek, M., Thies, J.
Stable Video Portraits
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), October 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
ps
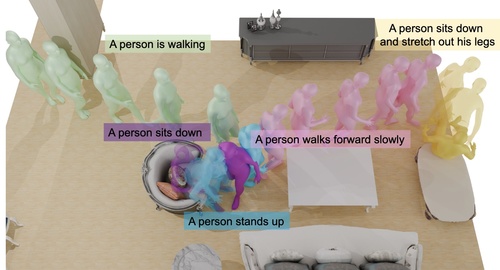
Yi, H., Thies, J., Black, M. J., Peng, X. B., Rempe, D.
Generating Human Interaction Motions in Scenes with Text Control
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, October 2024 (inproceedings)
ps
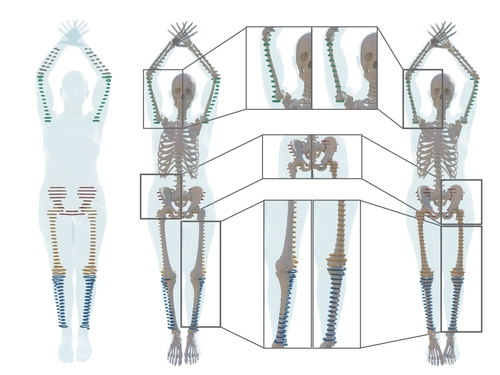
Dakri, A., Arora, V., Challier, L., Keller, M., Black, M. J., Pujades, S.
On predicting 3D bone locations inside the human body
In 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), October 2024 (inproceedings)
ncs
ps
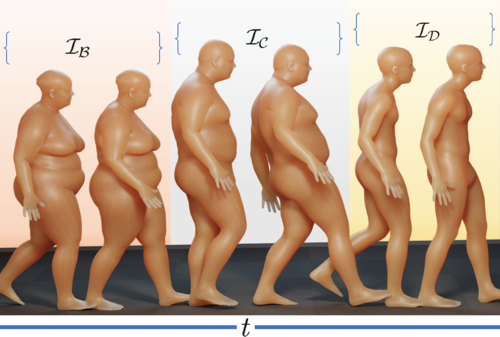
Ostrek, M., O’Sullivan, C., Black, M., Thies, J.
Synthesizing Environment-Specific People in Photographs
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), October 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
ps
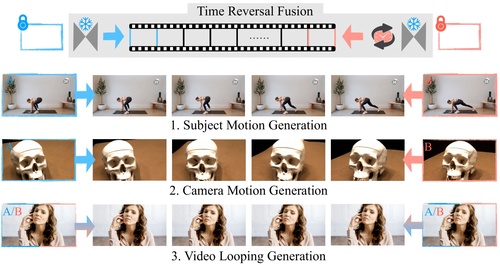
Feng, H., Ding, Z., Xia, Z., Niklaus, S., Fernandez Abrevaya, V., Black, M. J., Zhang, X.
Explorative Inbetweening of Time and Space
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, October 2024 (inproceedings)
sf
Dorner, F. E., Nastl, V. Y., Hardt, M.
Limits to Scalable Evaluation at the Frontier: LLM as Judge Won’t Beat Twice the Data
arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.13341, October 2024 (conference) Submitted
ps
Tripathi, S., Taheri, O., Lassner, C., Black, M. J., Holden, D., Stoll, C.
HUMOS: Human Motion Model Conditioned on Body Shape
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, October 2024 (inproceedings)
sf
Dominguez-Olmedo, R., Dorner, F. E., Hardt, M.
Training on the Test Task Confounds Evaluation and Emergence
arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.07890, October 2024 (conference) In revision
rm
Yoder, Z., Rumley, E., Schmidt, I., Rothemund, P., Keplinger, C.
Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules for rapidly reconfigurable high-speed robots
Science Robotics, 9, September 2024 (article)
ps
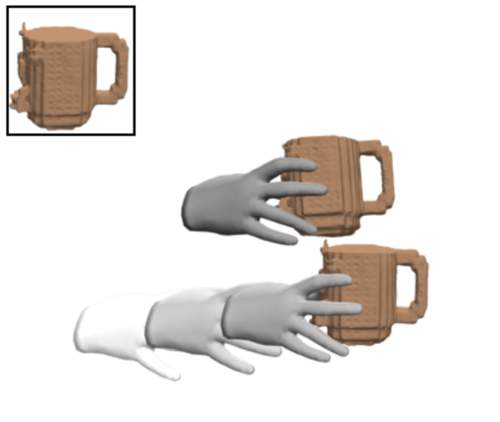
Zhang, H., Christen, S., Fan, Z., Hilliges, O., Song, J.
GraspXL: Generating Grasping Motions for Diverse Objects at Scale
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, September 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
hi
ei
OS Lab
zwe-sw
Cao, C. G. L., Javot, B., Bhattarai, S., Bierig, K., Oreshnikov, I., Volchkov, V. V.
Fiber-Optic Shape Sensing Using Neural Networks Operating on Multispecklegrams
IEEE Sensors Journal, 24(17):27532-27540, September 2024 (article)
ps
Sanyal, S.
Leveraging Unpaired Data for the Creation of Controllable Digital Humans
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems and Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, September 2024 (phdthesis) To be published
sf
Nastl, V. Y., Hardt, M.
Predictors from Causal Features Do Not Generalize Better to New Domains
arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09891, September 2024 (conference) Accepted
ps
Sun, J., Huang, L., Hongsong Wang, C. Z. J. Q., Islam, M. T., Xie, E., Zhou, B., Xing, L., Chandrasekaran, A., Black, M. J.
Localization and recognition of human action in 3D using transformers
Nature Communications Engineering , 13(125), September 2024 (article)
ps
Osman, A. A. A.
Realistic Digital Human Characters: Challenges, Models and Algorithms
University of Tübingen, September 2024 (phdthesis)
hi
rm
Sanchez-Tamayo, N., Yoder, Z., Rothemund, P., Ballardini, G., Keplinger, C., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Cutaneous Electrohydraulic (CUTE) Wearable Devices for Pleasant Broad-Bandwidth Haptic Cues
Advanced Science, (2402461):1-14, September 2024 (article)
rm
Buchner, T. J. K., Fukushima, T., Kazemipour, A., Gravert, S., Prairie, M., Romanescu, P., Arm, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, S. L., Walter, J., Keplinger, C., Katzschmann, R. K.
Electrohydraulic Musculoskeletal Robotic Leg for Agile, Adaptive, yet Energy-Efficient Locomotion
Nature Communications, 15(1), September 2024 (article)
hi
Tashiro, N., Faulkner, R., Melnyk, S., Rodriguez, T. R., Javot, B., Tahouni, Y., Cheng, T., Wood, D., Menges, A., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Building Instructions You Can Feel: Edge-Changing Haptic Devices for Digitally Guided Construction
ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, September 2024 (article) Accepted
sf
Cruz, A. F., Hardt, M., Mendler-Dünner, C.
Evaluating Language Models as Risk Scores
arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.14614, September 2024 (conference) Accepted
ei
Schumacher, P., Krause, L., Schneider, J., Büchler, D., Martius, G., Haeufle, D.
Learning to Control Emulated Muscles in Real Robots: Towards Exploiting Bio-Inspired Actuator Morphology
In 10th International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), September 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted
ps
Fan, Z., Ohkawa, T., Yang, L., Lin, N., Zhou, Z., Zhou, S., Liang, J., Gao, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Li, F., Zheng, L., Lu, F., Zeid, K. A., Leibe, B., On, J., Baek, S., Prakash, A., Gupta, S., He, K., Sato, Y., Hilliges, O., Chang, H. J., Yao, A.
Benchmarks and Challenges in Pose Estimation for Egocentric Hand Interactions with Objects
In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024), LNCS, Springer Cham, September 2024 (inproceedings) Accepted