Reinforcement Learning and Control
Model-based Reinforcement Learning and Planning
Object-centric Self-supervised Reinforcement Learning
Self-exploration of Behavior
Causal Reasoning in RL
Equation Learner for Extrapolation and Control
Intrinsically Motivated Hierarchical Learner
Regularity as Intrinsic Reward for Free Play
Curious Exploration via Structured World Models Yields Zero-Shot Object Manipulation
Natural and Robust Walking from Generic Rewards
Goal-conditioned Offline Planning
Offline Diversity Under Imitation Constraints
Learning Diverse Skills for Local Navigation
Learning Agile Skills via Adversarial Imitation of Rough Partial Demonstrations
Combinatorial Optimization as a Layer / Blackbox Differentiation
Object-centric Self-supervised Reinforcement Learning
Symbolic Regression and Equation Learning
Representation Learning
Stepsize adaptation for stochastic optimization
Probabilistic Neural Networks
Learning with 3D rotations: A hitchhiker’s guide to SO(3)
Motion Blur in Layers
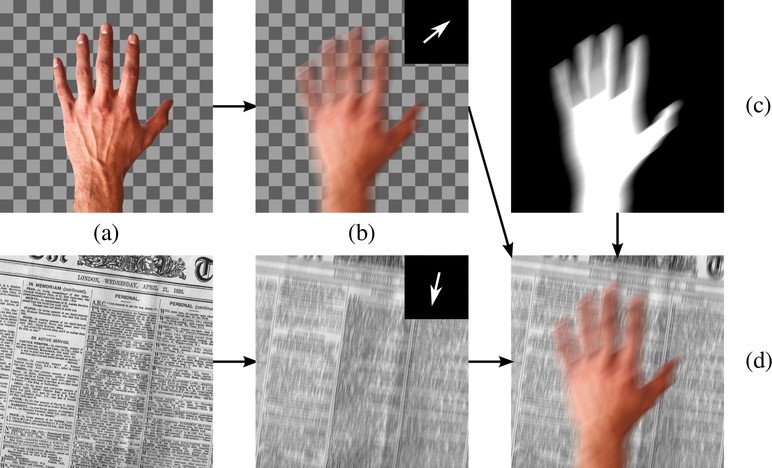
Videos contain complex spatially-varying motion blur due to the combination of object motion, camera motion, and depth variation with finite shutter speeds. Existing methods to estimate optical flow, deblur the images, and segment the scene fail in such cases. In particular, boundaries between differently moving objects cause problems, because here the blurred images are a combination of the blurred appearances of multiple surfaces. We address this with a novel layered model of scenes in motion. From a motion-blurred video sequence, we jointly estimate the layer segmentation and each layer’s appearance and motion. Since the blur is a function of the layer motion and segmentation, it is completely determined by our generative model. Given a video, we formulate the optimization problem as minimizing the pixel error between the blurred frames and images synthesized from the model, and solve it using gradient descent. We demonstrate our approach on synthetic and real sequences.
Video
Members
Publications

