Human Pose, Shape and Action
3D Pose from Images
2D Pose from Images
Beyond Motion Capture
Action and Behavior
Body Perception
Body Applications
Pose and Motion Priors
Clothing Models (2011-2015)
Reflectance Filtering
Learning on Manifolds
Markerless Animal Motion Capture
Multi-Camera Capture
2D Pose from Optical Flow
Body Perception
Neural Prosthetics and Decoding
Part-based Body Models
Intrinsic Depth
Lie Bodies
Layers, Time and Segmentation
Understanding Action Recognition (JHMDB)
Intrinsic Video
Intrinsic Images
Action Recognition with Tracking
Neural Control of Grasping
Flowing Puppets
Faces
Deformable Structures
Model-based Anthropometry
Modeling 3D Human Breathing
Optical flow in the LGN
FlowCap
Smooth Loops from Unconstrained Video
PCA Flow
Efficient and Scalable Inference
Motion Blur in Layers
Facade Segmentation
Smooth Metric Learning
Robust PCA
3D Recognition
Object Detection
Intrinsic Properties of Scenes
Intrinsic images correspond to physical properties of the scene. It is a long-standing hypothesis that these fundamental scene properties provide a foundation for scene interpretation.
To decouple albedo and shading given a single image, we introduce a novel prior on albedo, that models albedo values as being drawn from a sparse set of basis colors []. This results in a Random Field model with global, latent variables (basis colors) and pixel-accurate output albedo values. We show that without edge information high-quality results can be achieved, that are on par with methods exploiting this source of information. Finally, we can improve on state-of-the-art results by integrating edge information into our model.
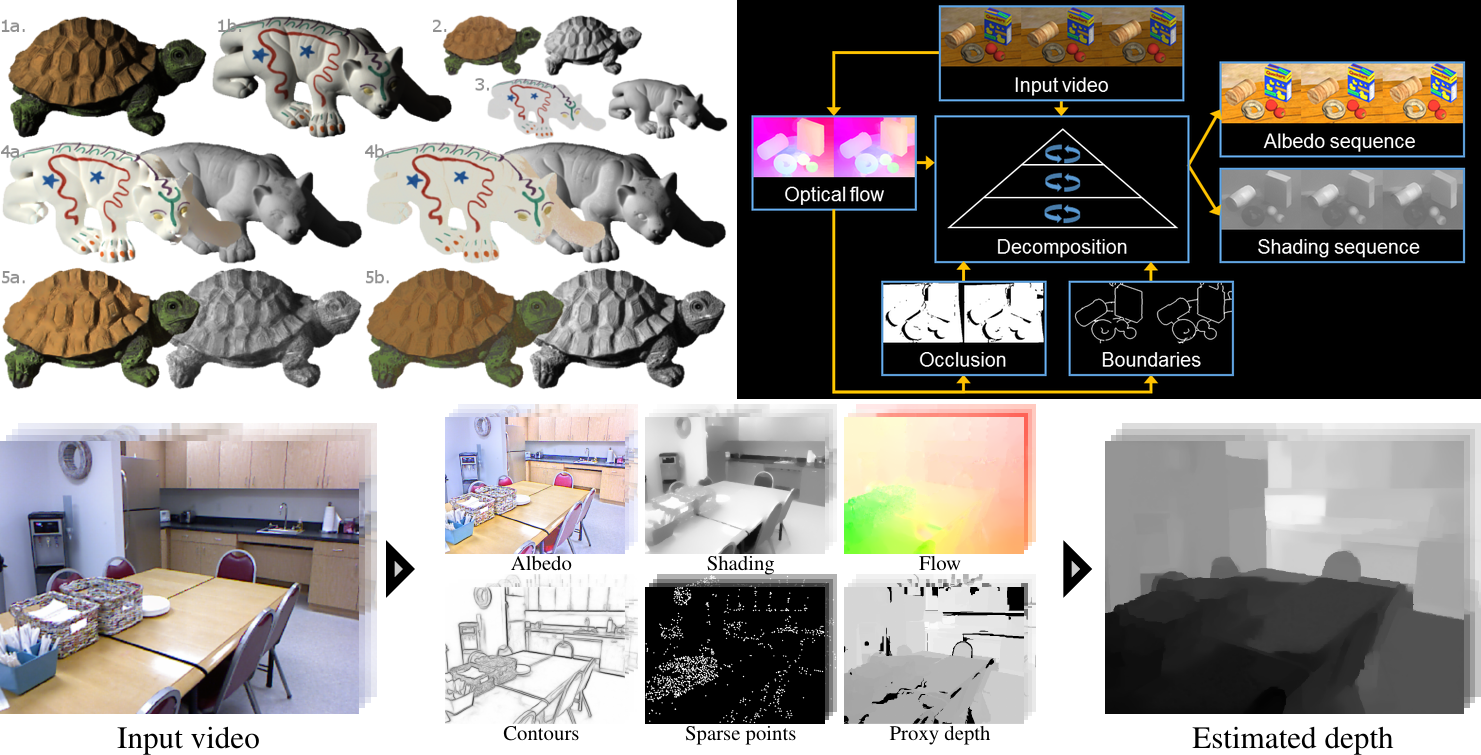
While today intrinsic images are typically taken to mean albedo and shading, the original meaning includes additional images related to object shape, such as surface boundaries, occluding regions, and depth. By using sequences of images, rather than static images, we extract a richer set of intrinsic images that include: albedo, shading, optical flow, occlusion regions, and motion boundaries. Intrinsic Video [] estimates temporally coherent albedo and shading sequences from video by exploiting the fact that albedo is constant over time while shading changes slowly. The approach makes only weak assumptions about the scene and substantially outperforms existing single-frame intrinsic image methods on complex video sequences.
Intrinsic Depth [] steps towards a more integrated treatment of intrinsic images. Our approach synergistically integrates the estimation of multiple intrinsic images including albedo, shading, optical flow, surface contours, and depth. We build upon an example-based framework for depth estimation that uses label transfer from a database of RGB and depth pairs. We also integrate sparse structure from motion to improve the metric accuracy of the estimated depth. We find that combining the estimation of multiple intrinsic images improves depth estimation relative to the baseline method.
Members
Publications




