Human Pose, Shape and Action
3D Pose from Images
2D Pose from Images
Beyond Motion Capture
Action and Behavior
Body Perception
Body Applications
Pose and Motion Priors
Clothing Models (2011-2015)
Reflectance Filtering
Learning on Manifolds
Markerless Animal Motion Capture
Multi-Camera Capture
2D Pose from Optical Flow
Body Perception
Neural Prosthetics and Decoding
Part-based Body Models
Intrinsic Depth
Lie Bodies
Layers, Time and Segmentation
Understanding Action Recognition (JHMDB)
Intrinsic Video
Intrinsic Images
Action Recognition with Tracking
Neural Control of Grasping
Flowing Puppets
Faces
Deformable Structures
Model-based Anthropometry
Modeling 3D Human Breathing
Optical flow in the LGN
FlowCap
Smooth Loops from Unconstrained Video
PCA Flow
Efficient and Scalable Inference
Motion Blur in Layers
Facade Segmentation
Smooth Metric Learning
Robust PCA
3D Recognition
Object Detection
Bodies from RGB-D
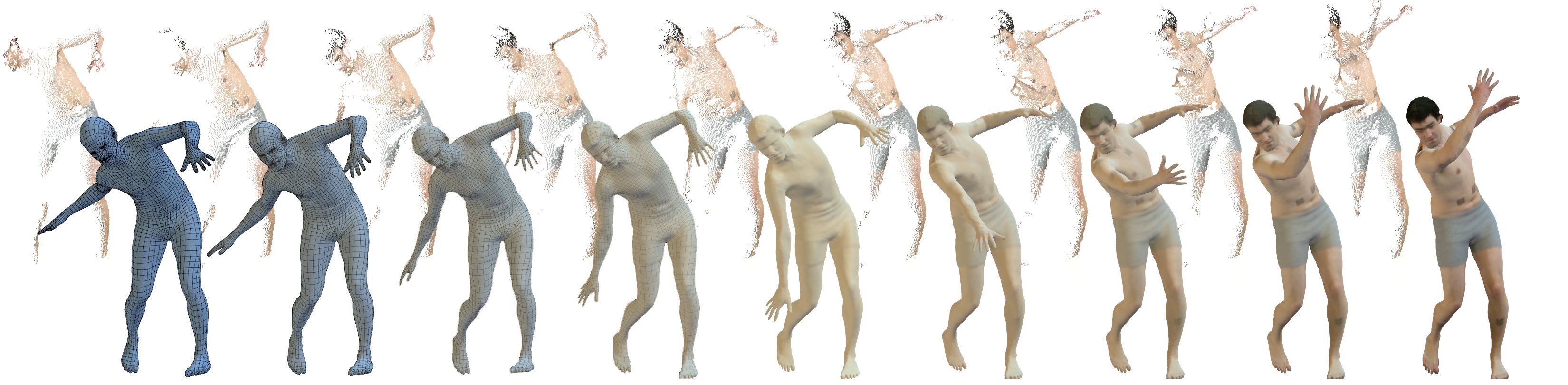

Accurate 3D body shape and appearance capture is useful for applications ranging from special effects, to fashion, to medicine. High-resolution scanners can capture human body shape and texture in great detail but these are bulky and expensive. In contrast, inexpensive RGB-D sensors are proliferating but are of much lower resolution. Scanning a full body from multiple partial views requires that the subject stands still or that the system precisely registers deforming point clouds captured from a non-rigid and articulated body.
We developed the first method to estimate human body shape from Kinect data []. The approach fits a body model to depth and image silhouettes to estimate body shape and pose from static scans of a subject in one or more static poses. We have since improved this greatly and our latest method estimates body shape with the realism of a high-resolution body scanner by allowing a user to move freely in front of a single commodity RGB-D sensor [
]
To achieve this, we develop a new parametric 3D body model, Delta, that is based on SCAPE but contains several important innovations. First, we define a parametric shape model at multiple resolutions that enables the estimation of body shape and pose in a coarse-to-fine process. Second, we define a variable-detail shape model that models facial shape with higher detail than body shape; this is important for realistic avatars. Third, we combine a relatively-low polygon count mesh with a high-resolution displacement map to capture realistic shape details, and a high-resolution texture map estimated from the sequence.
We bring color and range data in each frame into alignment with our body model adopting a coarse-to-fine approach. The method exploits geometry and image texture over time to obtain accurate shape, pose, and appearance information despite unconstrained motion, partial views, varying resolution, occlusion, and soft tissue deformation.
Our recovered models are competitive with high-resolution scans from a professional 3D scanning system. Our system creates accurate 3D avatars from challenging motion sequences and even captures soft tissue dynamics.
Members
Publications